Farming remarks
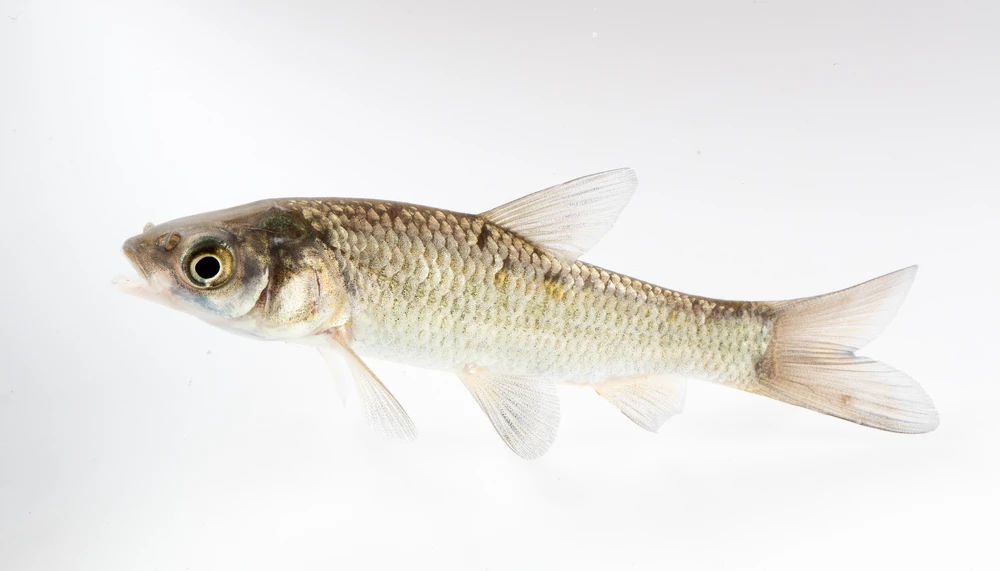
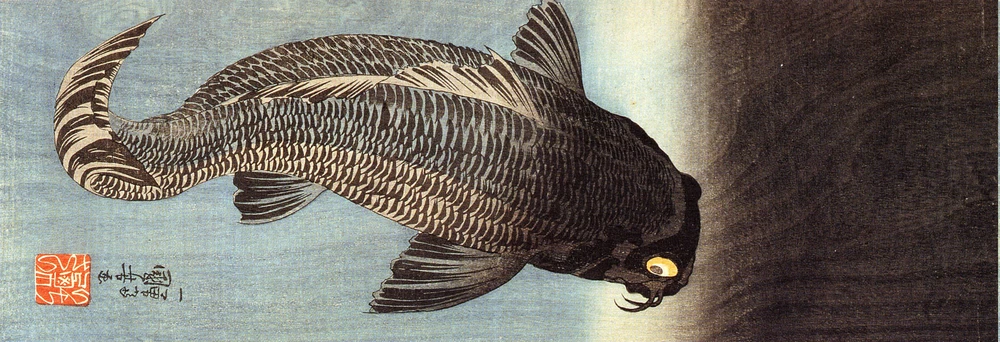
Mylopharyngodon piceus is a freshwater carp native to rivers and lakes of Asia that was introduced in Europe, the United States, and other countries. This species is a carnivorous bottom-dweller fish that does not leap out of the water and, consequently, is not easily detected or caught in large and deep rivers. M. piceus is considered one of the four Chinese major carps (among Hypophthalmichthys molitrix, H. nobilis, and Ctenopharyngodon idella), which has a high growth rate and an apparent great invasion potential.
Large JUVENILES and ADULTS use their heavy pharyngeal teeth to crash molluscs shells, mainly feeding on these animals. Thus, besides culturing M. piceus to sell as meat because of its good flavour and highly marketable potential, this species is also cultured in polycultures with other carps or other fish species for biological control, to feed from molluscs (mainly gastropods) that are potential intermediate hosts for diseases or that can cause other problems. In the United States, this species is mostly used for snail control in catfish ponds. SPAWNERS migrate upstream during spring to early summer to spawn in open and turbid waters. An increase in the river flow is the key triggering factor to spawning. Wild information about this carp species is rare and much information related to farm conditions is also still missing, especially related to aggression, substrate, stress response, malformations, and slaughter process. Further research about basic information from wild and cultured M. piceus is needed.
For details see: WelfareCheck | farm (latest major release: 2021-07-18)
Related news
In our FishTalk podcast, please find new episodes of the FishEthoBase programme here. Series 7 is about Bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis), Black carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus), and Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). In just a few words - less than 3 min - you will learn about natural needs, behaviours or farming conditions of the species to accompany their profile in the FishEthoBase.





Probably, we updated the profile. Check the version number in the head of the page. For more information on the version, see the FAQ about this. Why do we update profiles? Not just do we want to include new research that has come out, but we are continuously developing the database itself. For example, we changed the structure of entries in criteria or we added explanations for scores in the WelfareCheck | farm. And we are always refining our scoring rules.
The centre of the Overview is an array of criteria covering basic features and behaviours of the species. Each of this information comes from our literature search on the species. If we researched a full Dossier on the species, probably all criteria in the Overview will be covered and thus filled. This was our way to go when we first set up the database.
Because Dossiers are time consuming to research, we switched to focusing on WelfareChecks. These are much shorter profiles covering just 10 criteria we deemed important when it comes to behaviour and welfare in aquaculture (and lately fisheries, too). Also, WelfareChecks contain the assessment of the welfare potential of a species which has become the main feature of the fair-fish database over time. Because WelfareChecks do not cover as many criteria as a Dossier, we don't have the information to fill all blanks in the Overview, as this information is "not investigated by us yet".
Our long-term goal is to go back to researching Dossiers for all species covered in the fair-fish database once we set up WelfareChecks for each of them. If you would like to support us financially with this, please get in touch at ffdb@fair-fish.net
See the question "What does "not investigated by us yet" mean?". In short, if we have not had a look in the literature - or in other words, if we have not investigated a criterion - we cannot know the data. If we have already checked the literature on a criterion and could not find anything, it is "no data found yet". You spotted a "no data found yet" where you know data exists? Get in touch with us at ffdb@fair-fish.net!
First up, you will find answers to questions for the specific page you are on. Scrolling down in the FAQ window, there are also answers to more general questions. Explore our website and the other sub pages and find there the answers to questions relevant for those pages.
In the fair-fish database, when you have chosen a species (either by searching in the search bar or in the species tree), the landing page is an Overview, introducing the most important information to know about the species that we have come across during our literatures search, including common names, images, distribution, habitat and growth characteristics, swimming aspects, reproduction, social behaviour but also handling details. To dive deeper, visit the Dossier where we collect all available ethological findings (and more) on the most important aspects during the life course, both biologically and concerning the habitat. In contrast to the Overview, we present the findings in more detail citing the scientific references.
Depending on whether the species is farmed or wild caught, you will be interested in different branches of the database.
Farm branch
Founded in 2013, the farm branch of the fair-fish database focuses on farmed aquatic species.
Catch branch
Founded in 2022, the catch branch of the fair-fish database focuses on wild-caught aquatic species.
The heart of the farm branch of the fair-fish database is the welfare assessment – or WelfareCheck | farm – resulting in the WelfareScore | farm for each species. The WelfareCheck | farm is a condensed assessment of the species' likelihood and potential for good welfare in aquaculture, based on welfare-related findings for 10 crucial criteria (home range, depth range, migration, reproduction, aggregation, aggression, substrate, stress, malformations, slaughter).
For those species with a Dossier, we conclude to-be-preferred farming conditions in the Advice | farm. They are not meant to be as detailed as a rearing manual but instead, challenge current farming standards and often take the form of what not to do.
In parallel to farm, the main element of the catch branch of the fair-fish database is the welfare assessment – or WelfareCheck | catch – with the WelfareScore | catch for each species caught with a specific catching method. The WelfareCheck | catch, too, is a condensed assessment of the species' likelihood and potential for good welfare – or better yet avoidance of decrease of good welfare – this time in fisheries. We base this on findings on welfare hazards in 10 steps along the catching process (prospection, setting, catching, emersion, release from gear, bycatch avoidance, sorting, discarding, storing, slaughter).
In contrast to the farm profiles, in the catch branch we assess the welfare separately for each method that the focus species is caught with. In the case of a species exclusively caught with one method, there will be one WelfareCheck, whereas in other species, there will be as many WelfareChecks as there are methods to catch the species with.
Summarising our findings of all WelfareChecks | catch for one species in Advice | catch, we conclude which catching method is the least welfare threatening for this species and which changes to the gear or the catching process will potentially result in improvements of welfare.
Welfare of aquatic species is at the heart of the fair-fish database. In our definition of welfare, we follow Broom (1986): “The welfare of an individual is its state as regards its attempts to cope with its environment.” Thus, welfare may be perceived as a continuum on which an individual rates “good” or “poor” or everything in between.
We pursue what could be called a combination of not only a) valuing the freedom from injuries and stress (function-based approach) but b) supporting attempts to provide rewarding experiences and cognitive challenges (feelings-based approach) as well as c) arguing for enclosures that mimic the wild habitat as best as possible and allow for natural behaviour (nature-based approach).
Try mousing over the element you are interested in - oftentimes you will find explanations this way. If not, there will be FAQ on many of the sub-pages with answers to questions that apply to the respective sub-page. If your question is not among those, contact us at ffdb@fair-fish.net.
It's right here! We decided to re-name it to fair-fish database for several reasons. The database has grown beyond dealing purely with ethology, more towards welfare in general – and so much more. Also, the partners fair-fish and FishEthoGroup decided to re-organise their partnership. While maintaining our friendship, we also desire for greater independence. So, the name "fair-fish database" establishes it as a fair-fish endeavour.


