Information
Author: João L. Saraiva
Version: B | 1.2Published: 2024-12-31
- minor editorial changes (incl. correction of domestication level) plus new side note "Commercial relevance"
WelfareScore | farm
The score card gives our welfare assessments for aquatic species in 10 criteria.
For each criterion, we score the probability to experience good welfare under minimal farming conditions ("Likelihood") and under high-standard farming conditions ("Potential") representing the worst and best case scenario. The third dimension scores how certain we are of our assessments based on the number and quality of sources we found ("Certainty").
The WelfareScore sums just the "High" scores in each dimension. Although good welfare ("High") seems not possible in some criteria, there could be at least a potential improvement from low to medium welfare (indicated by ➚ and the number of criteria).
- Li = Likelihood that the individuals of the species experience good welfare under minimal farming conditions
- Po = Potential of the individuals of the species to experience good welfare under high-standard farming conditions
➚ = potential improvements not reaching "High" - Ce = Certainty of our findings in Likelihood and Potential
WelfareScore = Sum of criteria scoring "High" (max. 10 per dimension)
General remarks
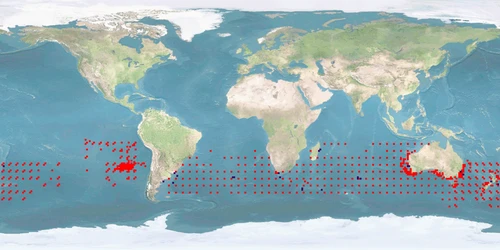
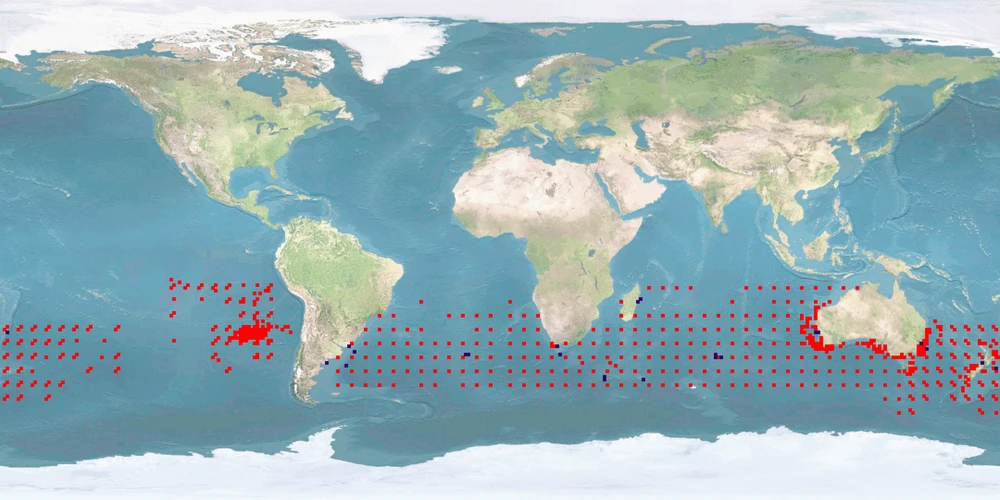
Farming of Thunnus maccoyii started in the 1970s mainly in Australia and Japan as a solution for the observed depletion of stocks and its high market value. This warm-blooded fish is an ocean cruiser, and therefore solutions for farming will be hampered by its need for space. There is already a fair amount of research on this species, but more knowledge is necessary regarding social interactions, stress, malformations, and on the development of a humane stunning and slaughter method. Although it is mostly farmed from wild-caught IND, rearing and housing of SPAWNERS should be improved.
1 Home range
Many species traverse in a limited horizontal space (even if just for a certain period of time per year); the home range may be described as a species' understanding of its environment (i.e., its cognitive map) for the most important resources it needs access to.
What is the probability of providing the species' whole home range in captivity?
It is low for minimal and high-standard farming conditions. Our conclusion is based on a high amount of evidence.


2 Depth range
Given the availability of resources (food, shelter) or the need to avoid predators, species spend their time within a certain depth range.
What is the probability of providing the species' whole depth range in captivity?
It is unclear for minimal farming conditions. It is medium for high-standard farming conditions. Our conclusion is based on a medium amount of evidence.


3 Migration
Some species undergo seasonal changes of environments for different purposes (feeding, spawning, etc.), and to move there, they migrate for more or less extensive distances.
What is the probability of providing farming conditions that are compatible with the migrating or habitat-changing behaviour of the species?
It is low for minimal and high-standard farming conditions. Our conclusion is based on a medium amount of evidence.


4 Reproduction
A species reproduces at a certain age, season, and sex ratio and possibly involving courtship rituals.
What is the probability of the species reproducing naturally in captivity without manipulation of these circumstances?
It is low for minimal farming conditions. It is medium for high-standard farming conditions. Our conclusion is based on a high amount of evidence.


5 Aggregation
Species differ in the way they co-exist with conspecifics or other species from being solitary to aggregating unstructured, casually roaming in shoals or closely coordinating in schools of varying densities.
What is the probability of providing farming conditions that are compatible with the aggregation behaviour of the species?
It is unclear for minimal farming conditions. It is high for high-standard farming conditions. Our conclusion is based on a medium amount of evidence.


6 Aggression
There is a range of adverse reactions in species, spanning from being relatively indifferent towards others to defending valuable resources (e.g., food, territory, mates) to actively attacking opponents.
What is the probability of the species being non-aggressive and non-territorial in captivity?
There are no findings for minimal and high-standard farming conditions.


7 Substrate
Depending on where in the water column the species lives, it differs in interacting with or relying on various substrates for feeding or covering purposes (e.g., plants, rocks and stones, sand and mud, turbidity).
What is the probability of providing the species' substrate and shelter needs in captivity?
It is high for minimal and high-standard farming conditions. Our conclusion is based on a high amount of evidence.


8 Stress
Farming involves subjecting the species to diverse procedures (e.g., handling, air exposure, short-term confinement, short-term crowding, transport), sudden parameter changes or repeated disturbances (e.g., husbandry, size-grading).
What is the probability of the species not being stressed?
It is unclear for minimal farming conditions. It is medium for high-standard farming conditions. Our conclusion is based on a low amount of evidence.


9 Malformations
Deformities that – in contrast to diseases – are commonly irreversible may indicate sub-optimal rearing conditions (e.g., mechanical stress during hatching and rearing, environmental factors unless mentioned in crit. 3, aquatic pollutants, nutritional deficiencies) or a general incompatibility of the species with being farmed.
What is the probability of the species being malformed rarely?
It is unclear for minimal and high-standard farming conditions. Our conclusion is based on a low amount of evidence.


10 Slaughter
The cornerstone for a humane treatment is that slaughter a) immediately follows stunning (i.e., while the individual is unconscious), b) happens according to a clear and reproducible set of instructions verified under farming conditions, and c) avoids pain, suffering, and distress.
What is the probability of the species being slaughtered according to a humane slaughter protocol?
It is low for minimal farming conditions. It is medium for high-standard farming conditions. Our conclusion is based on a medium amount of evidence.


Side note: Domestication
Teletchea and Fontaine introduced 5 domestication levels illustrating how far species are from having their life cycle closed in captivity without wild input, how long they have been reared in captivity, and whether breeding programmes are in place.
What is the species’ domestication level?
DOMESTICATION LEVEL 2 27, level 5 being fully domesticated.
Side note: Forage fish in the feed
450-1,000 milliard wild-caught fishes end up being processed into fish meal and fish oil each year which contributes to overfishing and represents enormous suffering. There is a broad range of feeding types within species reared in captivity.
To what degree may fish meal and fish oil based on forage fish be replaced by non-forage fishery components (e.g., poultry blood meal) or sustainable sources (e.g., soybean cake)?
WILD: carnivorous 18. FARM: JUVENILES and ADULTS are fed with baitfish 28 2, SPAWNERS with pilchards and squid 2; replacement of fish meal and fish oil is not reported.
Side note: Commercial relevance
How much is this species farmed annually?
8,252 t/year 1990-2019 amounting to estimated <1,000,000 IND/year 1990-2019 29.
Glossary
DOMESTICATION LEVEL 2 = part of the life cycle closed in captivity, also known as capture-based aquaculture 27
FARM = setting in farming environment or under conditions simulating farming environment in terms of size of facility or number of individuals
IND = individuals
JUVENILES = fully developed but immature individuals
LARVAE = hatching to mouth opening
OCEANODROMOUS = living and migrating in the sea
PLANKTONIC = horizontal movement limited to hydrodynamic displacement
SPAWNERS = adults during the spawning season; in farms: adults that are kept as broodstock
WILD = setting in the wild
Bibliography
2 Chen, Ben Nan, Wayne Hutchinson, and Craig Foster. 2015. Southern Bluefin Tuna Captive Breeding in Australia. In Advances in Tuna Aquaculture: From Hatchery to Market, 233.
3 Davis, Tim L. O., and Clive A. Stanley. 2002. Vertical and horizontal movements of southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii) in the Great Australian Bight observed with ultrasonic telemetry. Fishery Bulletin 100: 448–465.
4 Hayward, Craig J., Hamish M. Aiken, and Barbara F. Nowak. 2007. Metazoan parasites on gills of Southern Bluefin Tuna (Thunnus maccoyii) do not rapidly proliferate after transfer to sea cages. Aquaculture 262: 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.09.041.
5 Hayward, Craig J, Hamish M Aiken, and Barbara F Nowak. 2008. An epizootic of Caligus chiastos on farmed southern bluefin tuna Thunnus maccoyii off South Australia. Diseases of aquatic organisms 79: 57–63.
6 Pedersen, M. W., T. A. Patterson, U. H. Thygesen, and H. Madsen. 2011. Estimating animal behavior and residency from movement data. Oikos 120: 1281–1290. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2011.19044.x.
7 Lioka, C, K Kani, and H Nhhala. 2000. Present status and prospects of technical development of tuna sea-farming. Cahiers Options Méditerranéennes 47: 275–285.
8 Davis, Tim L. O., Greg P. Jenkins, and Jock W. Young. 1990. Diel patterns of vertical distribution in larvae of southern bluefin Thunnus maccoyii, and other tuna in the East Indian Ocean. Marine Ecology Progress Series 59: 63–74. https://doi.org/10.2307/24842422.
9 Patterson, Toby A., Karen Evans, Thor I. Carter, and John S. Gunn. 2008. Movement and behaviour of large southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii) in the Australian region determined using pop-up satellite archival tags. Fisheries Oceanography 17: 352–367. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2419.2008.00483.x.
10 Willis, Jay, John Phillips, Rachel Muheim, Francisco Javier Diego-Rasilla, and Alistair J. Hobday. 2009. Spike dives of juvenile southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii): a navigational role? Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 64: 57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-009-0818-2.
11 Glencross, Brett D., Steven M. Clarke, Jeffery G. Buchanan, Chris G. Carter, and Robert J. van Barneveld. 2002. Temporal Growth Patterns of Farmed Juvenile Southern Bluefin Tuna, Thunnus maccoyii (Castelnau) Fed Moist Pellets. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society 33: 138–145. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2002.tb00488.x.
12 Collette, B. B., and C. E. Nauen. 1983. FAO species catalogue. Vol. 2. Scombrids of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of tunas, mackerels, bonitos and related species known to date. Vol. 2. FAO Fisheries Synopsis 125. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
13 Hobday, Alistair, Karen Evans, J Eveson, Jessica Farley, Jason Hartog, Marinelle Basson, and Toby Patterson. 2015. Distribution and Migration—Southern Bluefin Tuna (Thunnus maccoyii). In Biology and Ecology of Bluefin Tuna, ed. Takashi Kitagawa and Shingo Kimura, 189–210. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/b18714-12.
14 Fujioka, Ko, Alistair J. Hobday, Ryo Kawabe, Kazushi Miyashita, Yoshimi Takao, Osamu Sakai, and Tomoyuki Itoh. 2012. Departure behaviour of juvenile southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii) from southern Western Australia temperate waters in relation to the Leeuwin Current. Fisheries Oceanography 21: 269–280. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2419.2012.00620.x.
15 Farley, Jessica H, and Tim L. O. Davis. 1998. Reproductive dynamics of Thunnus maccoyii. Fishery Bulletin 96: 223–236.
16 Evans, Karen, Toby A. Patterson, Howard Reid, and Shelton J. Harley. 2012. Reproductive Schedules in Southern Bluefin Tuna: Are Current Assumptions Appropriate? PLoS ONE 7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034550.
17 Davis, T. L. O., V. Lyne, and G. P. Jenkins. 1991. Advection, dispersion and mortality of a patch of southern bluefin tuna larvae Thunnus maccoyii in the East Indian Ocean. Marine Ecology Progress Series 73: 33–45. https://doi.org/10.2307/24825390.
18 Olson, Robert J. 1980. Synopsis of biological data on the southern bluefin tuna, Thunnus maccoyii (Castelnau, 1872).
19 Willis, Jay. 2008. Simulation model of universal law of school size distribution applied to southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii) in the Great Australian Bight. Ecological Modelling 213: 33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2008.01.017.
20 Newlands, Nathaniel K, and Tracy A Porcelli. 2008. Measurement of the size, shape and structure of Atlantic bluefin tuna schools in the open ocean. Fisheries Research 91: 42–55.
21 Thomas, P M, C G Carter, J F Carragher, and B D Glencross. 2003. Preliminary information on temporal changes in the blood chemistry of farmed southern bluefin tuna, Thunnus maccoyii (Castelnau), after feeding and repeated sampling disturbance. Aquaculture Research 34: 265–267. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2109.2003.00812.x.
22 Kirchhoff, Nicole T., Kirsty M. Rough, and Barbara F. Nowak. 2011. Moving Cages Further Offshore: Effects on Southern Bluefin Tuna, T. maccoyii, Parasites, Health and Performance. PLOS ONE 6: e23705. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0023705.
23 Woolley, Lindsey D., Stewart D. Fielder, and Jian G. Qin. 2013. Swimbladder inflation associated with body density change and larval survival in southern bluefin tuna Thunnus maccoyii. Aquaculture International 21: 1233–1242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9626-9.
24 Hilder, P. I. 2013. Development of vision and larval feeding responses in southern bluefin tuna and yellowtail kingfish. Phd, University of Tasmania.
25 EFSA. 2009. Species-specific welfare aspects of the main systems of stunning and killing of farmed tuna. EFSA Journal 1072: 1–53. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1072.
26 De La Gandara, F. 2015. Cultured Aquatic Species Information Programme. Thunnus thynnus. Rome: FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department.
27 Teletchea, Fabrice, and Pascal Fontaine. 2012. Levels of domestication in fish: implications for the sustainable future of aquaculture. Fish and Fisheries 15: 181–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12006.
28 Ellis, David, and Ilse Kiessling. 2015. Ranching of southern blufin tuna in Australia. In Advances in Tuna Aquaculture: From Hatchery to Market, 217.
29 Mood, Alison, Elena Lara, Natasha K. Boyland, and Phil Brooke. 2023. Estimating global numbers of farmed fishes killed for food annually from 1990 to 2019. Animal Welfare 32: e12. https://doi.org/10.1017/awf.2023.4.



Lorem ipsum
Something along the lines of: we were aware of the importance of some topics so that we wanted to include them and collect data but not score them. For WelfareChecks | farm, these topics are "domestication level", "feed replacement", and "commercial relevance". The domestication and commercial relevance aspects allow us to analyse the questions whether increasing rate of domestication or relevance in farming worldwide goes hand in hand with better welfare; the feed replacement rather goes in the direction of added suffering for all those species which end up as feed. For a carnivorous species, to gain 1 kg of meat, you do not just kill this one individual but you have to take into account the meat that it was fed during its life in the form of fish meal and fish oil. In other words, carnivorous species (and to a degree also omnivorous ones) have a larger "fish in:fish out" ratio.
Lorem ipsum
Probably, we updated the profile. Check the version number in the head of the page. For more information on the version, see the FAQ about this. Why do we update profiles? Not just do we want to include new research that has come out, but we are continuously developing the database itself. For example, we changed the structure of entries in criteria or we added explanations for scores in the WelfareCheck | farm. And we are always refining our scoring rules.
The centre of the Overview is an array of criteria covering basic features and behaviours of the species. Each of this information comes from our literature search on the species. If we researched a full Dossier on the species, probably all criteria in the Overview will be covered and thus filled. This was our way to go when we first set up the database.
Because Dossiers are time consuming to research, we switched to focusing on WelfareChecks. These are much shorter profiles covering just 10 criteria we deemed important when it comes to behaviour and welfare in aquaculture (and lately fisheries, too). Also, WelfareChecks contain the assessment of the welfare potential of a species which has become the main feature of the fair-fish database over time. Because WelfareChecks do not cover as many criteria as a Dossier, we don't have the information to fill all blanks in the Overview, as this information is "not investigated by us yet".
Our long-term goal is to go back to researching Dossiers for all species covered in the fair-fish database once we set up WelfareChecks for each of them. If you would like to support us financially with this, please get in touch at ffdb@fair-fish.net
See the question "What does "not investigated by us yet" mean?". In short, if we have not had a look in the literature - or in other words, if we have not investigated a criterion - we cannot know the data. If we have already checked the literature on a criterion and could not find anything, it is "no data found yet". You spotted a "no data found yet" where you know data exists? Get in touch with us at ffdb@fair-fish.net!
Once you have clicked on "show details", the entry for a criterion will unfold and display the summarised information we collected from the scientific literature – complete with the reference(s).
As reference style we chose "Springer Humanities (numeric, brackets)" which presents itself in the database as a number in a grey box. Mouse over the box to see the reference; click on it to jump to the bibliography at the bottom of the page. But what does "[x]-[y]" refer to?
This is the way we mark secondary citations. In this case, we read reference "y", but not reference "x", and cite "x" as mentioned in "y". We try to avoid citing secondary references as best as possible and instead read the original source ourselves. Sometimes we have to resort to citing secondarily, though, when the original source is: a) very old or not (digitally) available for other reasons, b) in a language no one in the team understands. Seldomly, it also happens that we are running out of time on a profile and cannot afford to read the original. As mentioned, though, we try to avoid it, as citing mistakes may always happen (and we don't want to copy the mistake) and as misunderstandings may occur by interpreting the secondarily cited information incorrectly.
If you spot a secondary reference and would like to send us the original work, please contact us at ffdb@fair-fish.net
In general, we aim at giving a good representation of the literature published on the respective species and read as much as we can. We do have a time budget on each profile, though. This is around 80-100 hours for a WelfareCheck and around 300 hours for a Dossier. It might thus be that we simply did not come around to reading the paper.
It is also possible, though, that we did have to make a decision between several papers on the same topic. If there are too many papers on one issue than we manage to read in time, we have to select a sample. On certain topics that currently attract a lot of attention, it might be beneficial to opt for the more recent papers; on other topics, especially in basic research on behaviour in the wild, the older papers might be the go-to source.
And speaking of time: the paper you are missing from the profile might have come out after the profile was published. For the publication date, please check the head of the profile at "cite this profile". We currently update profiles every 6-7 years.
If your paper slipped through the cracks and you would like us to consider it, please get in touch at ffdb@fair-fish.net
This number, for example "C | 2.1 (2022-11-02)", contains 4 parts:
- "C" marks the appearance – the design level – of the profile part. In WelfareChecks | farm, appearance "C" is our most recent one with consistent age class and label (WILD, FARM, LAB) structure across all criteria.
- "2." marks the number of major releases within this appearance. Here, it is major release 2. Major releases include e.g. changes of the WelfareScore. Even if we just add one paper – if it changes the score for one or several criteria, we will mark this as a major update for the profile. With a change to a new appearance, the major release will be re-set to 1.
- ".1" marks the number of minor updates within this appearance. Here, it is minor update 1. With minor updates, we mean changes in formatting, grammar, orthography. It can also mean adding new papers, but if these papers only confirm the score and don't change it, it will be "minor" in our book. With a change to a new appearance, the minor update will be re-set to 0.
- "(2022-11-02)" is the date of the last change – be it the initial release of the part, a minor, or a major update. The nature of the changes you may find out in the changelog next to the version number.
If an Advice, for example, has an initial release date and then just a minor update date due to link corrections, it means that – apart from correcting links – the Advice has not been updated in a major way since its initial release. Please take this into account when consulting any part of the database.
First up, you will find answers to questions for the specific page you are on. Scrolling down in the FAQ window, there are also answers to more general questions. Explore our website and the other sub pages and find there the answers to questions relevant for those pages.
In the fair-fish database, when you have chosen a species (either by searching in the search bar or in the species tree), the landing page is an Overview, introducing the most important information to know about the species that we have come across during our literatures search, including common names, images, distribution, habitat and growth characteristics, swimming aspects, reproduction, social behaviour but also handling details. To dive deeper, visit the Dossier where we collect all available ethological findings (and more) on the most important aspects during the life course, both biologically and concerning the habitat. In contrast to the Overview, we present the findings in more detail citing the scientific references.
Depending on whether the species is farmed or wild caught, you will be interested in different branches of the database.
Farm branch
Founded in 2013, the farm branch of the fair-fish database focuses on farmed aquatic species.
Catch branch
Founded in 2022, the catch branch of the fair-fish database focuses on wild-caught aquatic species.
The heart of the farm branch of the fair-fish database is the welfare assessment – or WelfareCheck | farm – resulting in the WelfareScore | farm for each species. The WelfareCheck | farm is a condensed assessment of the species' likelihood and potential for good welfare in aquaculture, based on welfare-related findings for 10 crucial criteria (home range, depth range, migration, reproduction, aggregation, aggression, substrate, stress, malformations, slaughter).
For those species with a Dossier, we conclude to-be-preferred farming conditions in the Advice | farm. They are not meant to be as detailed as a rearing manual but instead, challenge current farming standards and often take the form of what not to do.
In parallel to farm, the main element of the catch branch of the fair-fish database is the welfare assessment – or WelfareCheck | catch – with the WelfareScore | catch for each species caught with a specific catching method. The WelfareCheck | catch, too, is a condensed assessment of the species' likelihood and potential for good welfare – or better yet avoidance of decrease of good welfare – this time in fisheries. We base this on findings on welfare hazards in 10 steps along the catching process (prospection, setting, catching, emersion, release from gear, bycatch avoidance, sorting, discarding, storing, slaughter).
In contrast to the farm profiles, in the catch branch we assess the welfare separately for each method that the focus species is caught with. In the case of a species exclusively caught with one method, there will be one WelfareCheck, whereas in other species, there will be as many WelfareChecks as there are methods to catch the species with.
Summarising our findings of all WelfareChecks | catch for one species in Advice | catch, we conclude which catching method is the least welfare threatening for this species and which changes to the gear or the catching process will potentially result in improvements of welfare.
Welfare of aquatic species is at the heart of the fair-fish database. In our definition of welfare, we follow Broom (1986): “The welfare of an individual is its state as regards its attempts to cope with its environment.” Thus, welfare may be perceived as a continuum on which an individual rates “good” or “poor” or everything in between.
We pursue what could be called a combination of not only a) valuing the freedom from injuries and stress (function-based approach) but b) supporting attempts to provide rewarding experiences and cognitive challenges (feelings-based approach) as well as c) arguing for enclosures that mimic the wild habitat as best as possible and allow for natural behaviour (nature-based approach).
Try mousing over the element you are interested in - oftentimes you will find explanations this way. If not, there will be FAQ on many of the sub-pages with answers to questions that apply to the respective sub-page. If your question is not among those, contact us at ffdb@fair-fish.net.
It's right here! We decided to re-name it to fair-fish database for several reasons. The database has grown beyond dealing purely with ethology, more towards welfare in general – and so much more. Also, the partners fair-fish and FishEthoGroup decided to re-organise their partnership. While maintaining our friendship, we also desire for greater independence. So, the name "fair-fish database" establishes it as a fair-fish endeavour.